Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Traveling Salesman Problem#
This is an example of a drawing solution of the traveling salesman problem
The function used to produce the solution is
christofides(),
where given a set of nodes, it calculates the route of the nodes
that the traveler has to follow in order to minimize the total cost.
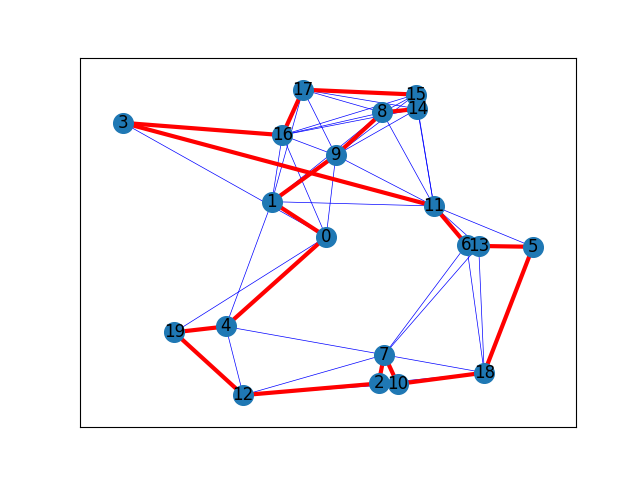
The route of the traveller is: [0, 4, 19, 12, 2, 7, 10, 18, 5, 13, 6, 11, 3, 16, 17, 15, 14, 8, 9, 1, 0]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import networkx as nx
import networkx.algorithms.approximation as nx_app
import math
G = nx.random_geometric_graph(20, radius=0.4, seed=3)
pos = nx.get_node_attributes(G, "pos")
# Depot should be at (0,0)
pos[0] = (0.5, 0.5)
H = G.copy()
# Calculating the distances between the nodes as edge's weight.
for i in range(len(pos)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(pos)):
dist = math.hypot(pos[i][0] - pos[j][0], pos[i][1] - pos[j][1])
dist = dist
G.add_edge(i, j, weight=dist)
cycle = nx_app.christofides(G, weight="weight")
edge_list = list(nx.utils.pairwise(cycle))
# Draw closest edges on each node only
nx.draw_networkx_edges(H, pos, edge_color="blue", width=0.5)
# Draw the route
nx.draw_networkx(
G,
pos,
with_labels=True,
edgelist=edge_list,
edge_color="red",
node_size=200,
width=3,
)
print("The route of the traveller is:", cycle)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.054 seconds)