Warning
This documents an unmaintained version of NetworkX. Please upgrade to a maintained version and see the current NetworkX documentation.
approximate_current_flow_betweenness_centrality¶
-
approximate_current_flow_betweenness_centrality(G, normalized=True, weight='weight', dtype=<type 'float'>, solver='full', epsilon=0.5, kmax=10000)[source]¶ Compute the approximate current-flow betweenness centrality for nodes.
Approximates the current-flow betweenness centrality within absolute error of epsilon with high probability [1].
Parameters: - G (graph) – A NetworkX graph
- normalized (bool, optional (default=True)) – If True the betweenness values are normalized by 2/[(n-1)(n-2)] where n is the number of nodes in G.
- weight (string or None, optional (default=’weight’)) – Key for edge data used as the edge weight. If None, then use 1 as each edge weight.
- dtype (data type (float)) – Default data type for internal matrices. Set to np.float32 for lower memory consumption.
- solver (string (default=’lu’)) – Type of linear solver to use for computing the flow matrix. Options are “full” (uses most memory), “lu” (recommended), and “cg” (uses least memory).
- epsilon (float) – Absolute error tolerance.
- kmax (int) – Maximum number of sample node pairs to use for approximation.
Returns: nodes – Dictionary of nodes with betweenness centrality as the value.
Return type: dictionary
Notes
The running time is
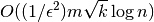 and the space required is
and the space required is 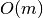 for n nodes and m edges.
for n nodes and m edges.If the edges have a ‘weight’ attribute they will be used as weights in this algorithm. Unspecified weights are set to 1.
References
[1] Ulrik Brandes and Daniel Fleischer: Centrality Measures Based on Current Flow. Proc. 22nd Symp. Theoretical Aspects of Computer Science (STACS ‘05). LNCS 3404, pp. 533-544. Springer-Verlag, 2005. http://www.inf.uni-konstanz.de/algo/publications/bf-cmbcf-05.pdf