Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Cycle Detection#
This example demonstrates the use of nx.find_cycle to find a single,
arbitrary cycle in a graph.
Other functions like nx.simple_cycles and nx.cycle_basis can be used to
find all cycles or a cycle basis.
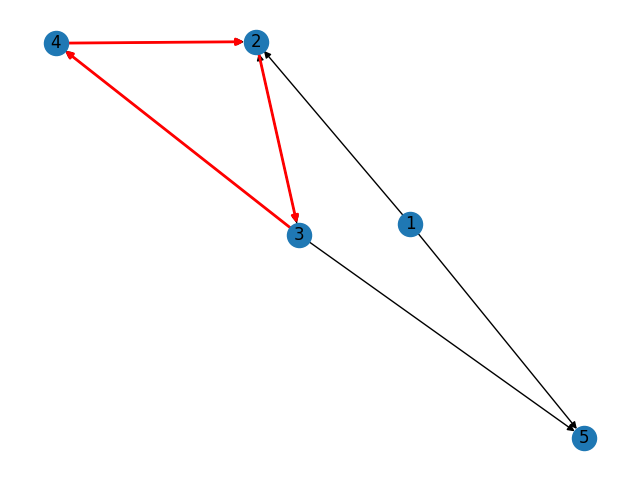
[(2, 3, 'forward'), (3, 4, 'forward'), (4, 2, 'forward')]
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create a simple directed graph with a cycle
G = nx.DiGraph([(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 2), (3, 5), (3, 2), (1, 5)])
# Draw the graph
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=8020)
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True)
# The `orientation` parameter can be used to determine how directed edges are
# treated and the reporting of edge direction in the cycle
cycle = nx.find_cycle(G, orientation="original")
print(cycle)
# Highlight the cycle in red
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, edgelist=cycle, edge_color="r", width=2)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.089 seconds)